3. Wax:
Controls the open time (the time the adhesive remains molten and workable) and viscosity of the hot melt. Waxes also affect the adhesive’s heat resistance and flexibility.
4. Additives:
These can include antioxidants (to prevent degradation), stabilizers (to improve thermal stability), pigments (for color), and fillers (to modify properties like viscosity or cost). Hot melt adhesive formulation is a complex science that balances these components.
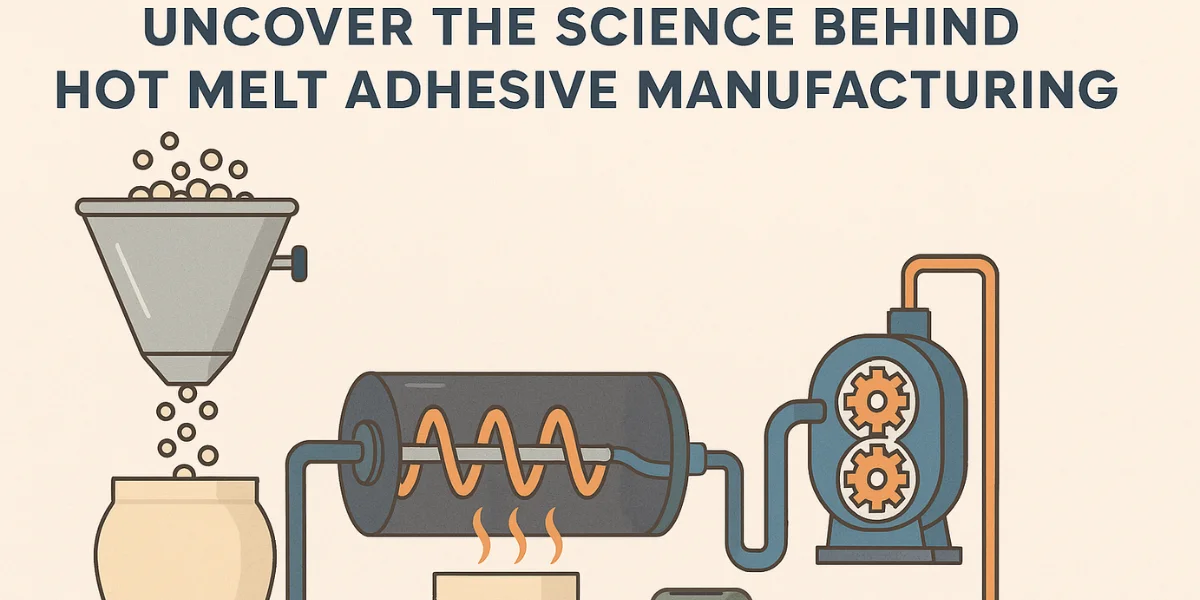
The manufacturing process of hot melt adhesives is a carefully controlled process that combines raw materials in precise ratios to achieve the desired performance characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages:
1. Adhesion Requirements:
The types of substrates the adhesive will bond to (e.g., paper, plastic, metal).
2. Temperature Resistance:
The operating temperatures to which the bond will be exposed.
3. Flexibility:
The need for a flexible or rigid bond.
4. Viscosity:
The desired flow properties of the molten adhesive.
5. Color:
Whether a clear, colored, or opaque adhesive is required.
Once selected, the raw materials are often pre-processed. This may involve:
1. Grinding or Pulverizing:
Reducing the size of solid raw materials to ensure proper mixing. Many HMAs are produced and sold as hot melt adhesive granules or pellets.
2. Melting Waxes:
Preparing waxes in a liquid form for easier incorporation.
3. Pre-blending Additives:
Combining minor additives to ensure uniform distribution.
This is the heart of the manufacturing process. The prepared raw materials are carefully weighed and added to a mixing vessel. The type of mixer used depends on the scale of production and the viscosity of the mixture. Common types of mixers include:
1. Sigma Blade Mixers:
These heavy-duty mixers are ideal for viscous materials and provide excellent mixing and kneading action.
2. High-Shear Mixers:
These mixers use a high-speed impeller to create intense shear forces, ensuring thorough mixing of ingredients.
3. Planetary Mixers:
These mixers have multiple mixing elements that rotate around a central axis, providing efficient mixing.
The mixing process is carefully controlled to ensure:
1. Homogeneous Distribution:
All ingredients are evenly dispersed throughout the mixture.
2. Proper Temperature Control:
Maintaining the correct temperature is critical to prevent degradation of the polymers and ensure proper melting and blending of the ingredients.
3. Shear Rate Optimization:
Applying the appropriate shear rate is essential for achieving the desired viscosity and particle size distribution.
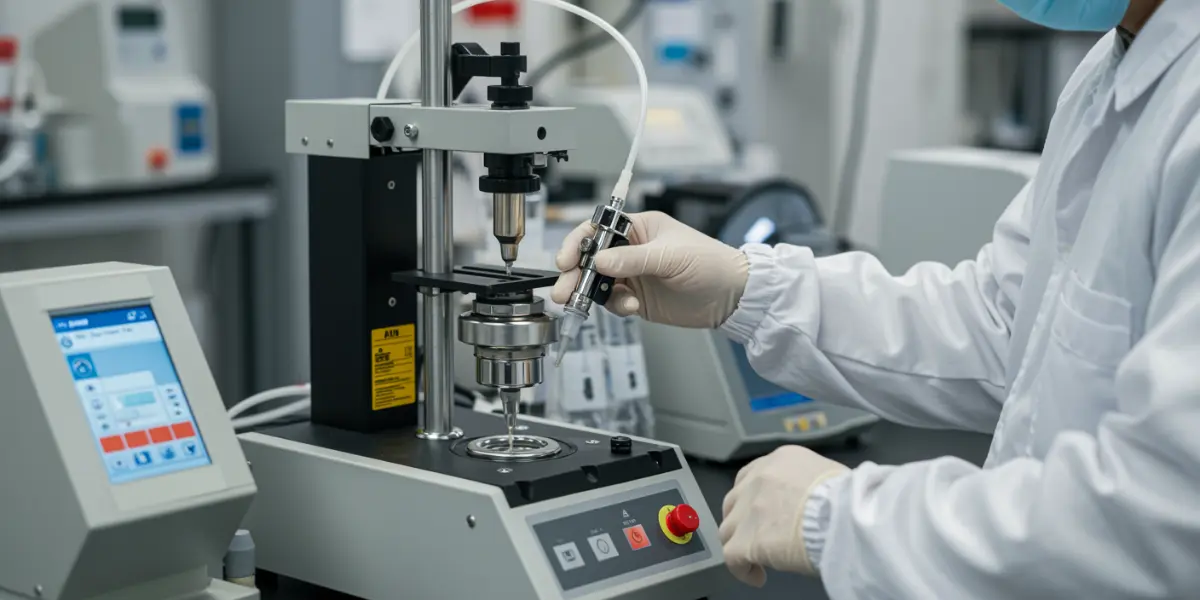
Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous hot melt adhesive quality control checks are performed to ensure the adhesive meets the required specifications. These tests may include:
1. Viscosity Measurement:
Determining the flow properties of the molten adhesive.
2. Softening Point Determination:
Measuring the temperature at which the adhesive begins to soften.
3. Tensile Strength Testing:
Assessing the strength of the adhesive bond.
4. Peel Strength Testing:
Measuring the force required to peel apart two bonded surfaces.
5. Color Measurement:
Ensuring the adhesive meets the specified color requirements.
6. Spectroscopic Analysis (FTIR, etc.):
Verifying the chemical composition of the adhesive.
Once the mixing and reaction stages are complete, the molten adhesive is typically filtered to remove any impurities or undissolved particles. This ensures a smooth, consistent product that will perform reliably in application. Filtration is usually carried out using fine mesh screens or filters.
The molten adhesive is then cooled and solidified into its final form. This can be achieved through various methods, including:
1. Casting:
Pouring the molten adhesive into molds to create solid blocks or slugs.
2. Extrusion:
Forcing the molten adhesive through a die to create rods, beads, or other shapes.
3. Pastillation:
Dropping small droplets of molten adhesive onto a cooling surface to form pellets.
4. Flaking:
Spreading a thin layer of molten adhesive onto a cooling drum to create flakes.
The cooling process is carefully controlled to prevent cracking or other defects.
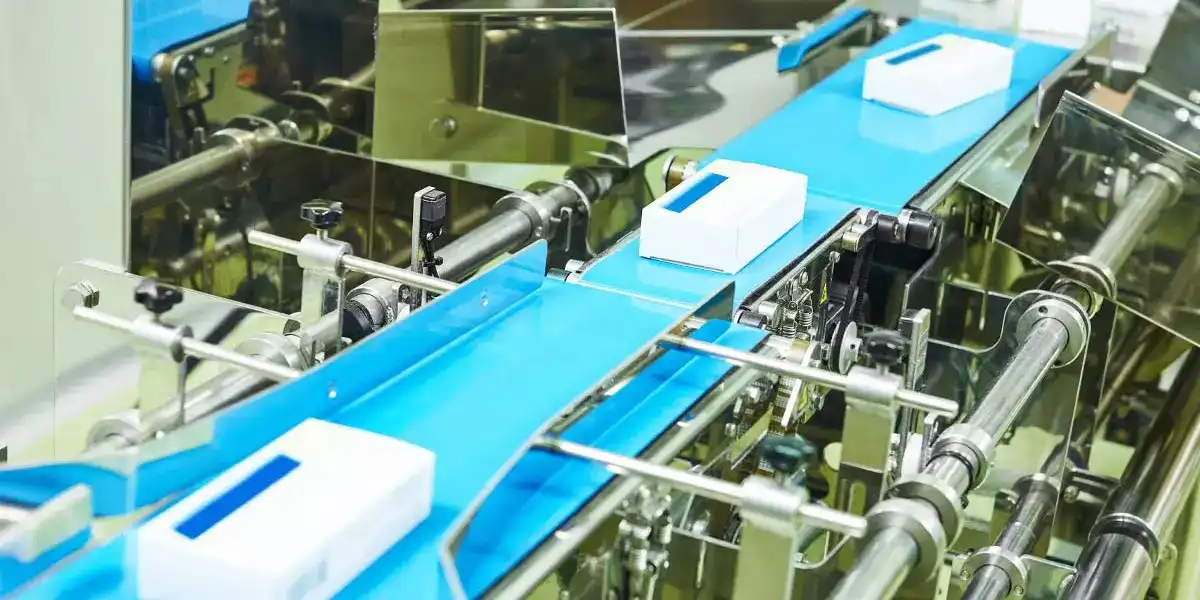
The solidified adhesive is then packaged in a variety of forms, depending on the intended application. Common packaging options include:
1. Cartridges:
For use in handheld applicators.
2. Drums:
For bulk dispensing.
3. Bags:
For loading into melting equipment.
4. Pellets:
For use in automated application systems.
5. Slugs/Sticks:
For smaller applications, often with glue guns.
The packaging is designed to protect the adhesive from moisture, contamination, and extreme temperatures.
Before being released for sale, the finished adhesive undergoes a final round of quality control testing to ensure it meets all specifications. This may include visual inspection, performance testing, and chemical analysis. Once the adhesive has passed all quality control checks, it is released for shipment to customers.
Hot melt adhesives are employed across a vast spectrum of industries due to their rapid bonding, versatility, and ease of use. Their ability to bond to a wide range of substrates makes them a go-to solution for numerous applications, driving growth in the hot melt adhesive market. This widespread adoption hinges significantly on maintaining hot melt adhesive quality across diverse hot melt adhesive uses. Here’s a glimpse into the diverse world of HMA applications:
2. Bookbinding:
HMAs provide a strong and flexible bond for book spines, holding pages together securely while allowing the book to open and close easily. They are used in both hardcover and softcover binding processes, where consistent hot melt adhesive quality is vital.
3. Woodworking:
HMAs are used for edge banding, profile wrapping, and general assembly in furniture manufacturing. They provide a quick and clean adhesive bonding solution for wood, particleboard, and MDF.
4. Automotive:
From bonding interior trim and carpets to assembling electronic components, HMAs play a vital role in automotive manufacturing. Their ability to withstand temperature fluctuations and vibrations makes them ideal for this demanding environment. The automotive industry requires HMAs with exceptional durability and consistent hot melt adhesive quality.
5. Electronics:
HMAs are used for potting and encapsulation of electronic components, providing protection against moisture, dust, and vibration. They also help to secure wires and cables within electronic devices. Proper adhesive bonding is crucial for the long-term performance of electronic assemblies.
6. Hygiene Products:
HMAs are essential in the manufacturing of diapers, feminine hygiene products, and other absorbent articles. They bond nonwoven materials, elastic, and absorbent cores together, ensuring comfort and functionality. These applications rely heavily on HMAs that are safe and maintain high hot melt adhesive quality.
7. Textiles:
HMAs are used for bonding fabrics, applying decorative elements, and creating fusible interlinings in the textile industry. They offer a durable and washable bond for a variety of textile materials.
8. Construction:
HMAs are used for bonding insulation materials, flooring, and wall panels in the construction industry. They provide a fast and efficient adhesive bonding solution for on-site assembly.
9. Medical:
HMAs are used in the assembly of medical devices, wound care products, and surgical drapes. They must meet stringent biocompatibility requirements for these applications. Given the sensitive nature of these applications, hot melt adhesive quality is of utmost importance.
10. DIY and Crafting:
HMAs are popular among hobbyists and crafters for a wide range of projects, from scrapbooking and jewelry making to home repairs and decorative crafts. Hot glue guns offer a convenient and easy-to-use application method for these applications.
As new materials and manufacturing processes emerge, the applications for HMAs continue to expand, contributing to the growth of the hot melt adhesive market and reinforcing their indispensable role in modern industry.
The hot melt adhesive manufacturing process is a complex and carefully controlled operation that requires expertise in chemistry, engineering, and materials science. Hot melt adhesive advantages include rapid bonding, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the different stages involved, you can gain a greater appreciation for the versatility and reliability of these essential bonding materials. From raw material selection to final packaging, each step plays a critical role in ensuring the performance and quality of the finished product. Whether it’s for packaging, product assembly, or other hot melt adhesive applications, hot melt adhesives continue to be a vital part of modern manufacturing.